java多线程创建方式四线程池
1、线程池的创建。
主要使用Executors工具类的以下静态方法:
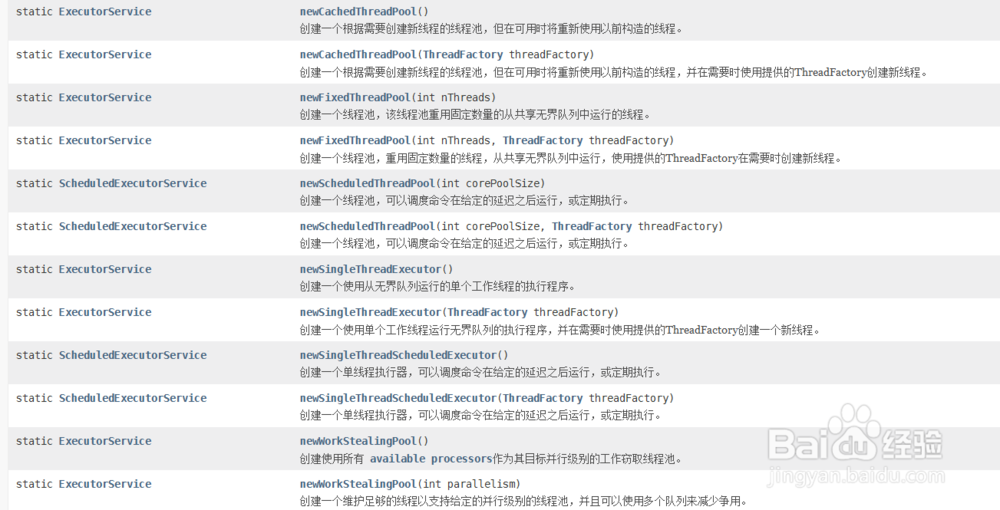
1、static ExecutorServicenewCachedThreadPool()
创建一个根据需要创建新线程的线程池,但在可用时将重新使用以前构造的线程。
2、static ExecutorServicenewCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
创建一个根据需要创建新线程的线程池,但在可用时将重新使用以前构造的线程,并在需要时使用提供的ThreadFactory创建新线程。
3、static ExecutorServicenewFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
创建一个线程池,该线程池重用固定数量的从共享无界队列中运行的线程。
4、static ExecutorServicenewFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
创建一个线程池,重用固定数量的线程,从共享无界队列中运行,使用提供的ThreadFactory在需要时创建新线程。
5、static ScheduledExecutorServicenewScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)
创建一个线程池,可以调度命令在给定的延迟之后运行,或定期执行。
6、static ScheduledExecutorServicenewScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
创建一个线程池,可以调度命令在给定的延迟之后运行,或定期执行。
7、static ExecutorServicenewSingleThreadExecutor()
创建一个使用从无界队列运行的单个工作线程的执行程序。
8、static ExecutorServicenewSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
创建一个使用单个工作线程运行无界队列的执行程序,并在需要时使用提供的ThreadFactory创建一个新线程。
9、static ScheduledExecutorServicenewSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()
创建一个单线程执行器,可以调度命令在给定的延迟之后运行,或定期执行。
10、static ScheduledExecutorServicenewSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
创建一个单线程执行器,可以调度命令在给定的延迟之后运行,或定期执行。
11、static ExecutorServicenewWorkStealingPool()
创建使用所有 available processors作为其目标并行级别的工作窃取线程池。
12、static ExecutorServicenewWorkStealingPool(int parallelism)
创建一个维护足够的线程以支持给定的并行级别的线程池,并且可以使用多个队列来减少争用。
2、创建线程池2:
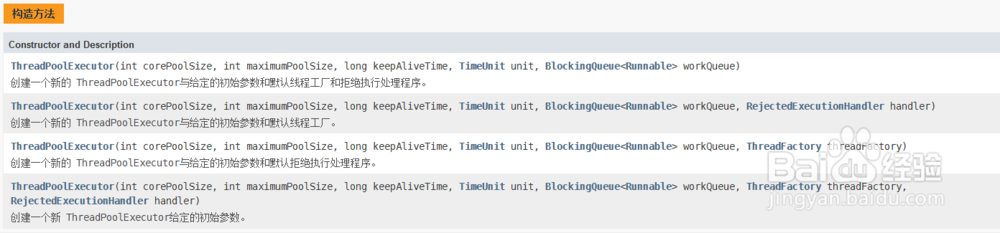
java.uitl.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor类是线程池中最核心的一个类
1、ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue)
创建一个新的 ThreadPoolExecutor与给定的初始参数和默认线程工厂和拒绝执行处理程序。
2、ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
创建一个新的 ThreadPoolExecutor与给定的初始参数和默认线程工厂。
3、ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
创建一个新的 ThreadPoolExecutor与给定的初始参数和默认拒绝执行处理程序。
4、ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
创建一个新 ThreadPoolExecutor给定的初始参数。
5、主要参数:
corePoolSize - 即使空闲时仍保留在池中的线程数,除非设置 allowCoreThreadTimeOut
maximumPoolSize - 池中允许的最大线程数
keepAliveTime - 当线程数大于核心时,这是多余的空闲线程在终止之前等待新任务的最大时间。
unit - keepAliveTime参数的时间单位
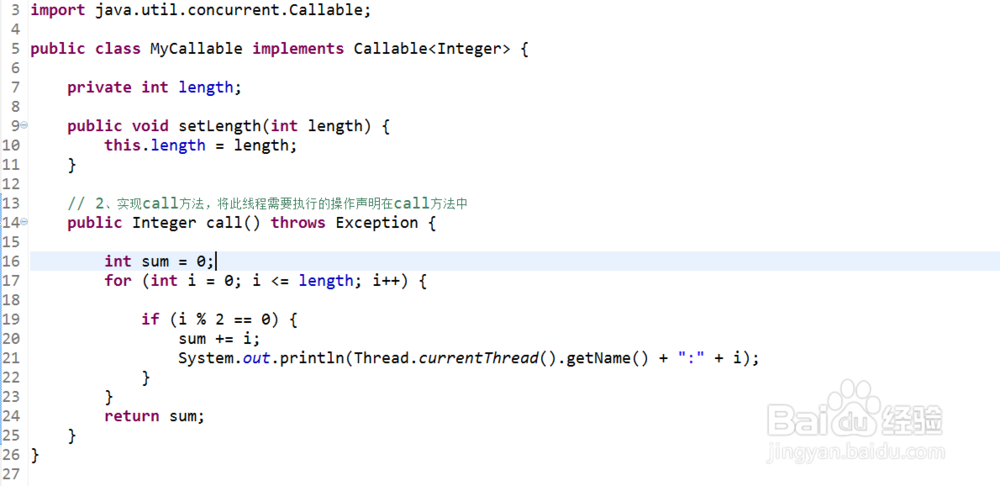
3、编写自己业务所需的Callable实现类
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
private int length;
public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
// 2、实现call方法,将此线程需要执行的操作声明在call方法中
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= length; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
sum += i;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}
}
return sum;
}
}
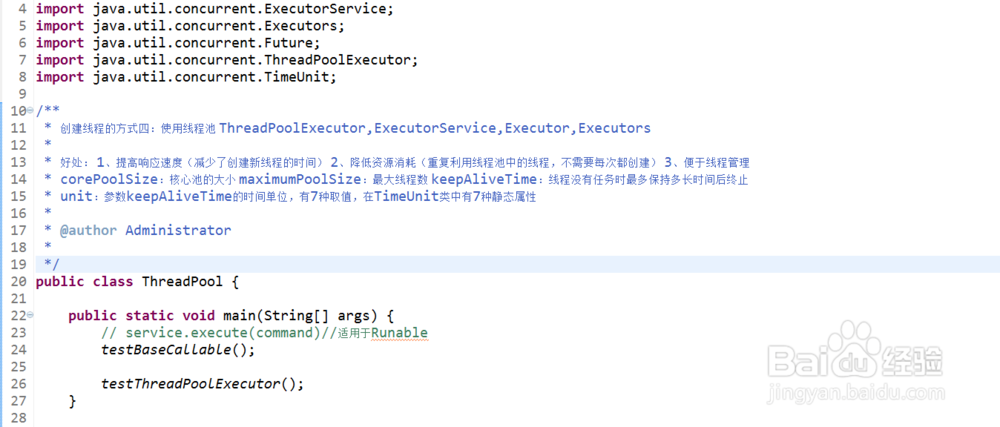
4、编写测试类
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 创建线程的方式四:使用线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor,ExecutorService,Executor,Executors
*
* 好处: 1、提高响应速度(减少了创建新线程的时间) 2、降低资源消耗(重复利用线程池中的线程,不需要每次都创建) 3、便于线程管理
* corePoolSize:核心池的大小 maximumPoolSize:最大线程数 keepAliveTime:线程没有任务时最多保持多长时间后终止
* unit:参数keepAliveTime的时间单位,有7种取值,在TimeUnit类中有7种静态属性
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// service.execute(command)//适用于Runable
testBaseCallable();
testThreadPoolExecutor();
}
// 1:测试线程池的基本使用
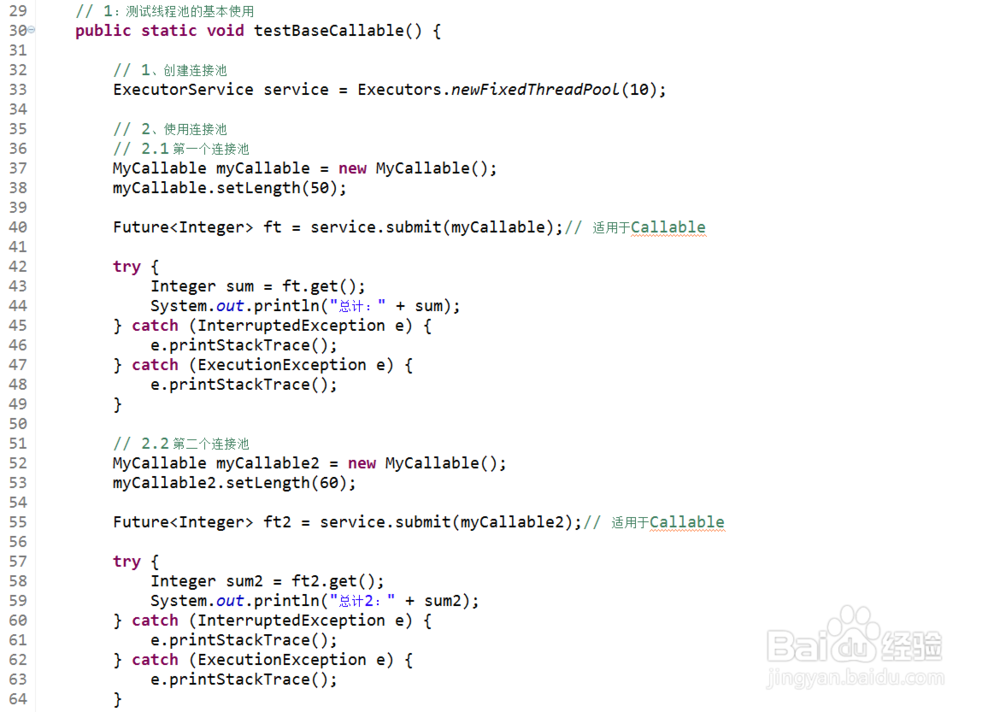
public static void testBaseCallable() {
// 1、创建连接池
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
// 2、使用连接池
// 2.1 第一个连接池
MyCallable myCallable = new MyCallable();
myCallable.setLength(50);
Future<Integer> ft = service.submit(myCallable);// 适用于Callable
try {
Integer sum = ft.get();
System.out.println("总计:" + sum);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 2.2 第二个连接池
MyCallable myCallable2 = new MyCallable();
myCallable2.setLength(60);
Future<Integer> ft2 = service.submit(myCallable2);// 适用于Callable
try {
Integer sum2 = ft2.get();
System.out.println("总计2:" + sum2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 3、关闭连接池
service.shutdown();
}
// 2:测试线程池参数的管理
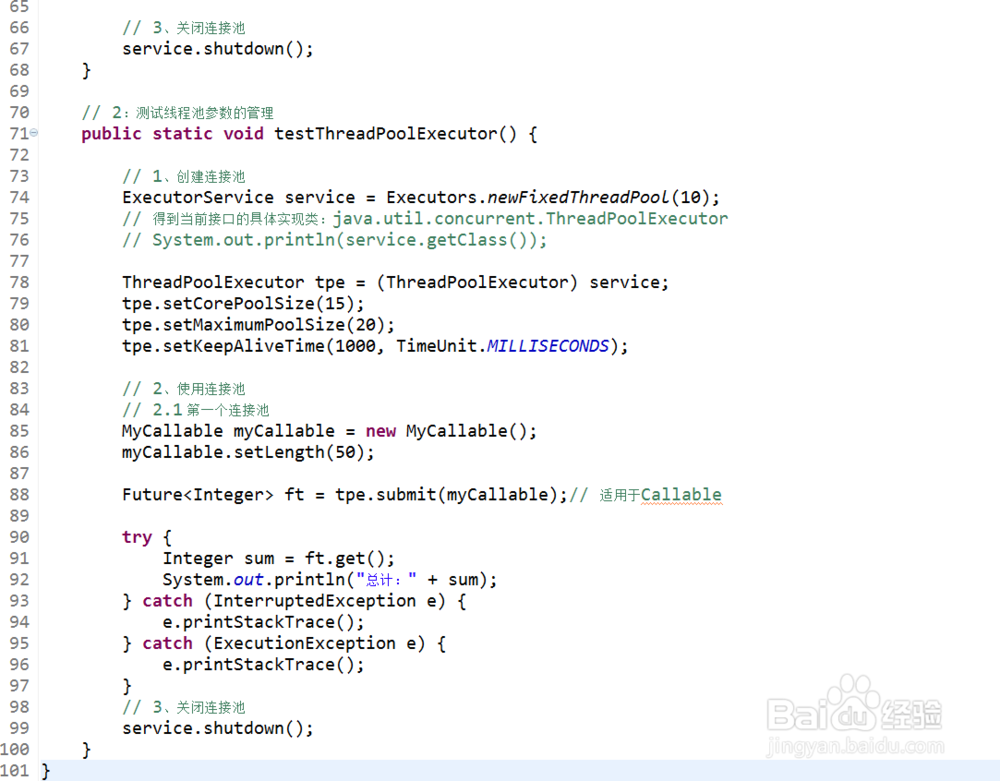
public static void testThreadPoolExecutor() {
// 1、创建连接池
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
// 得到当前接口的具体实现类:java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor
// System.out.println(service.getClass());
ThreadPoolExecutor tpe = (ThreadPoolExecutor) service;
tpe.setCorePoolSize(15);
tpe.setMaximumPoolSize(20);
tpe.setKeepAliveTime(1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 2、使用连接池
// 2.1 第一个连接池
MyCallable myCallable = new MyCallable();
myCallable.setLength(50);
Future<Integer> ft = tpe.submit(myCallable);// 适用于Callable
try {
Integer sum = ft.get();
System.out.println("总计:" + sum);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 3、关闭连接池
service.shutdown();
}
}
5、测试

6、县线程池单次请求超过线程最大数时,线程池将暂时不能执行的任务放入队列中,等有空闲线程时在执行。
package com.pa.executor;
import com.pa.common.MyCallable;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class ExecutorTest1 {
@Test
public void test1(){
Integer[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17};
System.out.println("详情打印:"+testArrayInteger(arrays));
}
public String testArrayInteger(Integer[] sum){
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
StringBuffer sf = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < sum.length; i++) {
MyCallable mc = new MyCallable();
mc.setLength(sum[i]);
Future<Integer> submit = executorService.submit(mc);
if(i%2==0){
submit.cancel(false);
continue;
}
Integer sum2 = null;
try {
sum2 = submit.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("数字"+sum[i]+"累加和为:" + sum2);
sf.append(sum2+",");
}
return sf.toString();
}
}
7、关键知识点介绍
1、Executors创建线程池当然使用ThreadPoolExecutor也可以创建线程池这个需要看具体需求。
2、ThreadPoolExecutor是ExecutorService接口的实现类,并且可以设置线程池的参数。