你知道Java中数字怎么比较大小吗?
1、先看个与预期一致的。
Show the code.
Code:
package chapter4;
/**
* Created by MyWorld on 2016/3/19.
*/
public class IntegerEqalsVerify {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer source = 127;
Integer target = 127;
boolean result = source == target;
System.out.println("scene 1:" + result);
boolean resultForEquals = source.equals(target);
System.out.println("scene 2:" + resultForEquals);
}
}

2、执行上面的代码。
都是true。这与我们的认知是一致的
Output:
scene 1:true
scene 2:true

3、把数字大小调整下,都改为128呢?
Code:
Integer source = 128;Integer target = 128;boolean result = source == target;

4、执行下,看看结果:
scene 1:false
scene 2:true
傻眼了吧。
为什么是false呢?

5、只要是比127大的数字。在上面的场景中,执行结果都是一样的
现在就来测个下限,先用数字-128.
执行一下。
可以看到,和平时的认知是一个的,都是true
Code:
Integer source = -128;
Integer target = -128;
boolean result = source == target;

6、改成-129。
看看执行结果:使用==比较时又不相等了。。。
scene 1:false
scene 2:true
Code:
Integer source = -129;
Integer target = -129;
boolean result = source == target;

7、为什么呢?
原因就出现在常量池了。
如果Integer的值在[-128,127]时,都会从常量池中取。
这样所有这个区间的Integer的对象是完全相同的,使用==比较肯定是true,因为内存地址是一样的的嘛
过了这个区间的,肯定不同了,不同的对象,内存地址不一样了的。
这种情况下,只能使用Equals来比较。
对象之间比较是否相等,一定要使用Equals
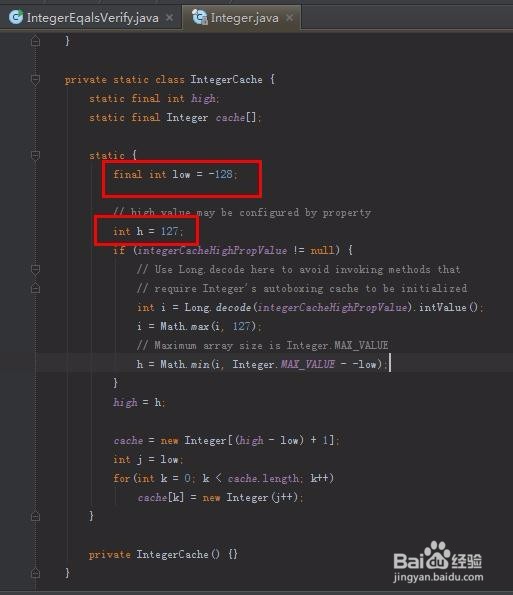
来一块看看java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
final int low = -128;
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
// Use Long.decode here to avoid invoking methods that
// require Integer's autoboxing cache to be initialized
int i = Long.decode(integerCacheHighPropValue).intValue();
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - -low);
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}