JAVA接口设计模式-工厂模式
1、首先来看一个简单的程序范例:在进行类设计的时候,要求需要有接口,而后接口要通过子类才可以进行对象的实例化处理。
传统代码开发:
package com.gwolf.springmvc.factory;
interface IFruit {//定义一个描述水果的操作
public void eat();//吃水果
}
class Apple implements IFruit {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("削皮吃苹果!");
}
}
public class FactoryDesign {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IFruit fruit = new Apple();
fruit.eat();
}
}
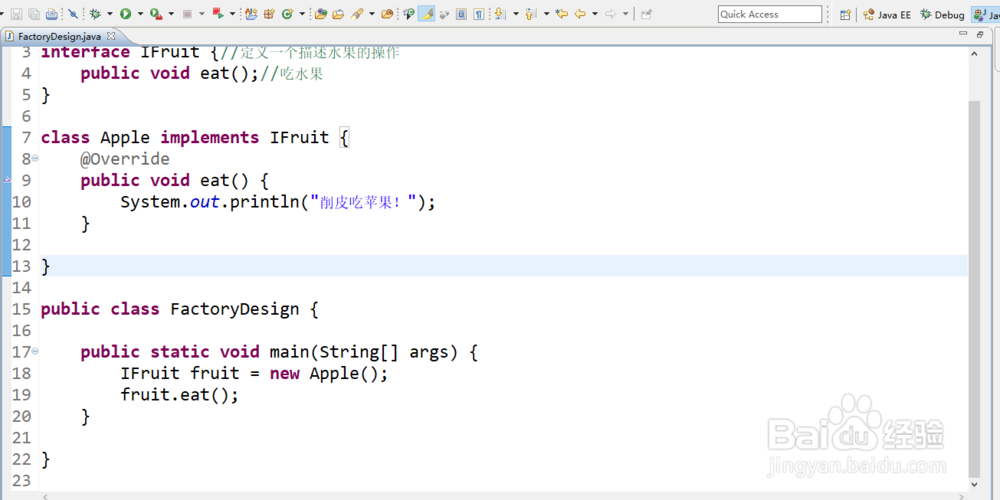
2、此时的程序实现的关键是:“IFruit fruit = new Apple();”,如果没有此语句,那么接口对象将无法进行实例化的操作处理。但是最大的败笔也在此。主方法是一个客户端,那么对于程序的修改不应该影响到客户端。假如我们又有了一个新的实现类:
package com.gwolf.springmvc.factory;
interface IFruit {//定义一个描述水果的操作
public void eat();//吃水果
}
class Apple implements IFruit {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("削皮吃苹果!");
}
}
class Orange implements IFruit {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("剥皮吃橘子!");
}
}
public class FactoryDesign {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IFruit fruit = new Apple();
fruit.eat();
}
}

3、假如我们需要吃橘子,我们需要修改客户端的代码。
java实现可移植性的关键是JVM,也就是说所有的程序都是在JVM上执行,而不同的操作系统中有匹配的JVM,那么相当于程序经过了JVM然后找到了操作系统。
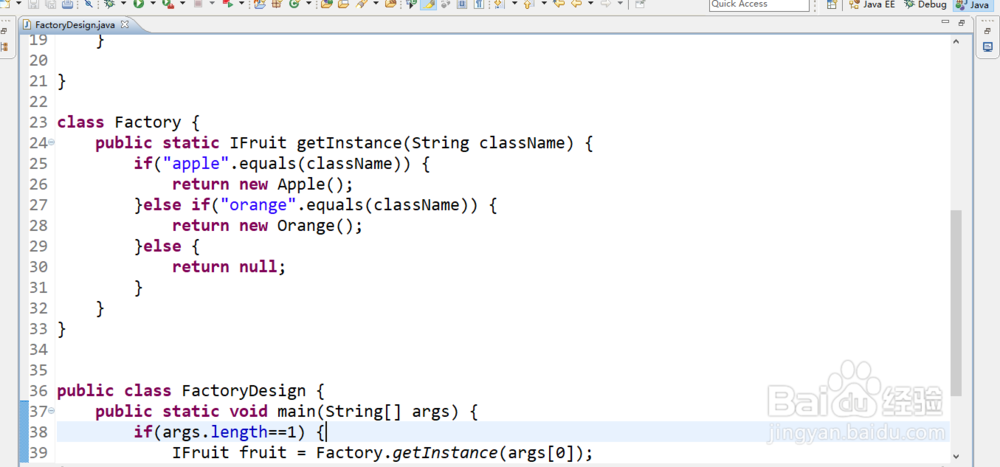
这个时候new是整个开发过程之中最大的耦合元凶,而我们在开发之中要想解耦合的关键在于要引入一个第三方,所以这个类可以使用Factory类描述。
class Factory {
public static IFruit getInstance(String className) {
if("apple".equals(className)) {
return new Apple();
}else if("orange".equals(className)) {
return new Orange();
}else {
return null;
}
}
}

4、这样我们在客户端就可以解耦对象的创建:
public class FactoryDesign {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length==1) {
IFruit fruit = Factory.getInstance(args[0]);
fruit.eat();
}
}
}

5、当更换使用的IFruit子类的时候主方法没有任何的变化就可以实现子类的变更,这样的设计就是工厂设计模式。
package com.gwolf.springmvc.factory;
interface IFruit {//定义一个描述水果的操作
public void eat();//吃水果
}
class Apple implements IFruit {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("削皮吃苹果!");
}
}
class Orange implements IFruit {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("剥皮吃橘子!");
}
}
class Factory {
public static IFruit getInstance(String className) {
if("apple".equals(className)) {
return new Apple();
}else if("orange".equals(className)) {
return new Orange();
}else {
return null;
}
}
}
public class FactoryDesign {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length==1) {
IFruit fruit = Factory.getInstance(args[0]);
fruit.eat();
}
}
}
6、以后只要是你编写的接口如果要想取得接口的实例化对象,第一反应就是写工厂类。
