如何用PYTHON解决有效的括号问题
1、打开JUPYTER NOTEBOOK,新建一个空白的PY文档。

2、s = "()"
if ("(" and ")" in s) or ("[" and "]" in s) or ("{" and "}" in s):
print(True)
else:
print(False)
很多同学会有多个IF来不断判断。

3、s = "(]"
if ("(" and ")" in s) or ("[" and "]" in s) or ("{" and "}" in s):
print(True)
else:
print(False)
但是这样容易出错也很麻烦。

4、s = "(]"
d = {"(": ")", "[": "]", "{": "}"}
dd = {}
for i in range(len(s)):
dd[s[i]] = s[i+1]
print(d)
print(dd)
于是开始有了字典储存符号的方法了。

5、s = "(]"
d = {"(": ")", "[": "]", "{": "}"}
if (len(s) % 2 != 0) or (len(s) == 0):
print(False)
else:
for i in range(len(s)):
if d[s[i]] != s[i+1]:
print(False)
break
else:
print(True)
我们首先要解决超出范围的问题。
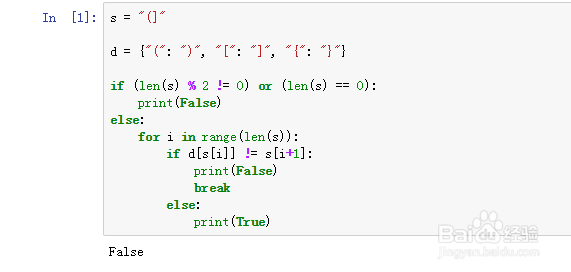
6、s = "()"
d = {"(": ")", "[": "]", "{": "}"}
if (len(s) % 2 != 0) or (len(s) == 0):
print(False)
else:
for i in range(len(s)):
if d[s[i]] != s[i+1]:
print(False)
break
else:
print(True)
break

7、s = "({[]})"
#it should be True.
d = {"(": ")", "[": "]", "{": "}"}
if (len(s) % 2 != 0) or (len(s) == 0):
print(False)
else:
for i in range(len(s)):
if d[s[i]] != s[i+1]:
print(False)
break
else:
print(True)
break
但是我们会发现这里就出错了。
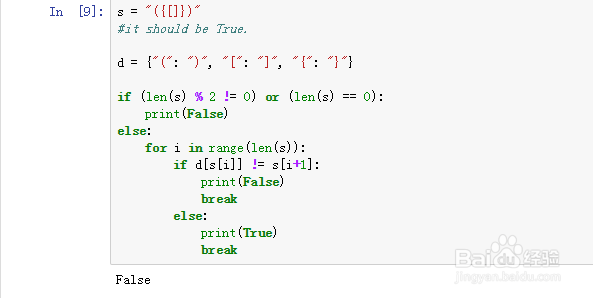
8、s = "({[]})"
#it should be True.
d = {'(': ')', '[': ']', '{': '}'}
if (len(s) % 2 != 0) or (len(s) == 0):
print(False)
else:
for i in range(len(s)):
for j in range(1, len(s)):
if s[i] == d[s[j]]:
print(True)
break
else:
print(False)
break
有些同学会用两个循环来解决。
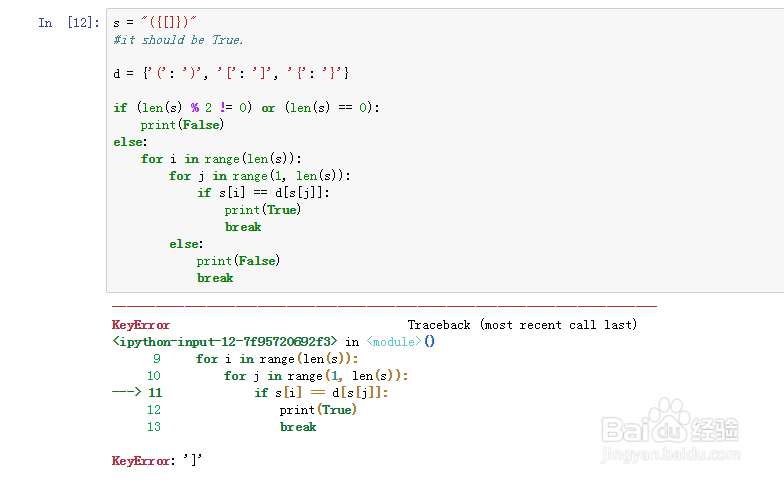
9、s = "()"
d = {')': '(', '}': '{', ']': '['}
temp = []
for i in s:
if i in d and d[i] == temp[len(temp)-1]:
temp.pop()
else:
temp.append(i)
if len(temp) == 0:
print(True)
else:
print(False)
但实际上简单的方法是要把字典的储存先更正过来。

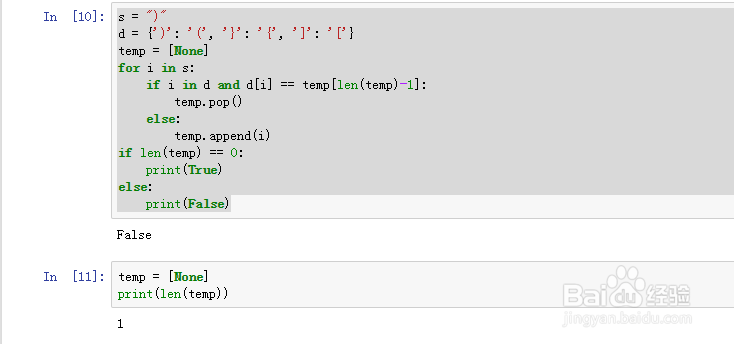
10、s = ")"
d = {')': '(', '}': '{', ']': '['}
temp = []
for i in s:
if i in d and d[i] == temp[len(temp)-1]:
temp.pop()
else:
temp.append(i)
if len(temp) == 0:
print(True)
else:
print(False)
s = ")"
d = {')': '(', '}': '{', ']': '['}
temp = [None]
for i in s:
if i in d and d[i] == temp[len(temp)-1]:
temp.pop()
else:
temp.append(i)
if len(temp) == 0:
print(True)
else:
print(False)
为了不超出范围,我们一定要设置NONE。

11、s = "()"
d = {')': '(', '}': '{', ']': '['}
temp = [None]
for i in s:
if i in d and d[i] == temp[len(temp)-1]:
temp.pop()
else:
temp.append(i)
if len(temp) == 1:
print(True)
else:
print(False)
最后要设置长度的判断,才可以。

