VC++6.0封装串口通讯类
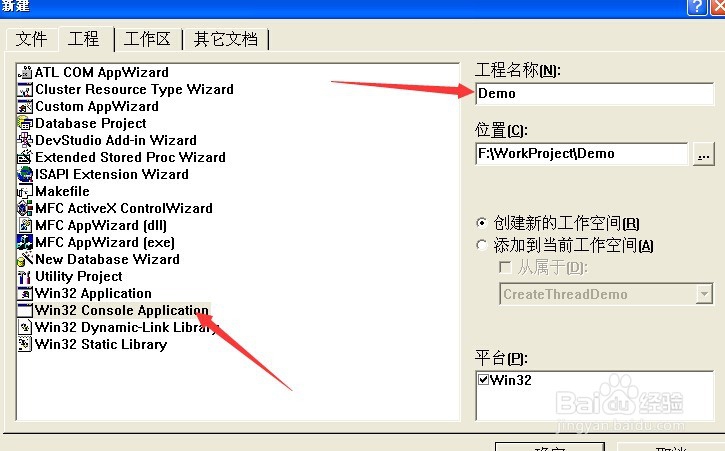
1、新建一个win32控制台程序
2、在类视图添加一个新类
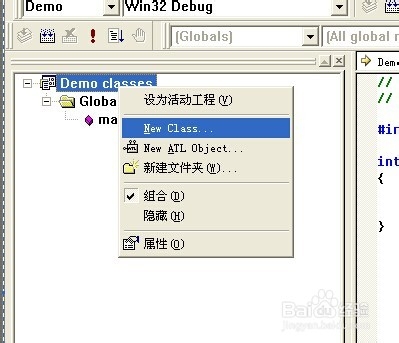
3、类的名字为:SerialPort

4、双击类名,在头文件中添加 方法声明.

5、在SerialPort.h中添加代码:
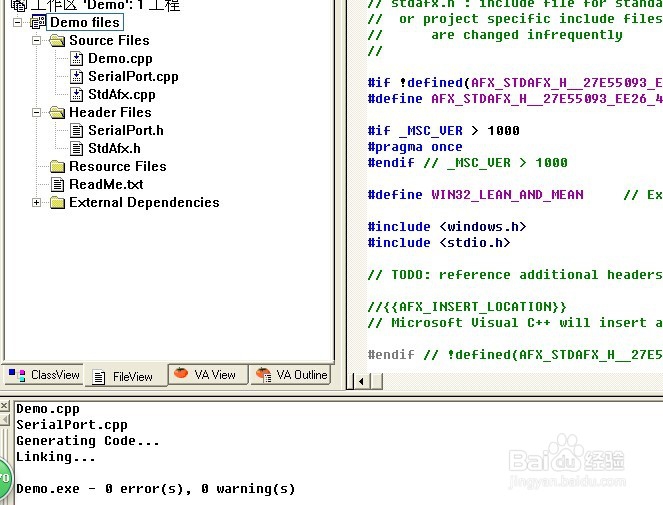
public:
//设置串口号
void setPortName(const int port);
//设置波特率
void setBaud( UINT baud );
//打开串口
BOOL InitPort( UINT portnr = 5, UINT baud = 9600, char parity = 'N', UINT databits = 8, UINT stopsbits = 1 );
//发送数据
int WriteToPort( char *writeData,int WriteSize );
//读取数据
int ReceiveChar( char *readBuff, int ReadSize );
//关闭串口
void ClosePort();
private:
HANDLE m_hComm; //串口句柄
COMMTIMEOUTS m_CommTimeouts;//超时时间
DCB m_dcb;//设置波特率 停止位 串口号码.....
int m_port; //串口号
UINT m_baud; //波特率

6、切换到文件视图 在SerialPort.cpp中实现声明的方法:

7、在SerialPort.cpp中添加代码:
SerialPort::SerialPort() //构造函数中初始化
{
m_hComm = NULL;
m_port = 1;
m_baud = 9600;
}
SerialPort::~SerialPort()//析构中释放
{
if (m_hComm != NULL)
{
CloseHandle(m_hComm);
m_hComm = NULL;
}
}
void SerialPort::setPortName( const int port)//设置串口号
{
m_port = port;
}
void SerialPort::setBaud( UINT baud )//设置波特率
{
m_baud = baud;
}
void SerialPort::ClosePort()//关闭串口
{
if (m_hComm != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
CloseHandle(m_hComm);
}
m_hComm = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
}
BOOL SerialPort::InitPort( UINT portnr, UINT baud, char parity, UINT databits, UINT stopsbits )//打开串口
{
//assert(portnr > 0 && portnr < 50);
char *szPort = new char[50];
char *szBaud = new char[50];
baud = m_baud;
portnr = m_port;
sprintf(szPort, "COM%d", portnr);
sprintf(szBaud, "baud=%d parity=%c data=%d stop=%d", baud, parity, databits, stopsbits);
if (m_hComm != NULL)
{
CloseHandle(m_hComm);
m_hComm = NULL;
}
m_hComm = CreateFile(szPort, // communication port string (COMX)
GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_WRITE, // read/write types
NULL, // comm devices must be opened with exclusive access
NULL, // no security attributes
OPEN_EXISTING, // comm devices must use OPEN_EXISTING
FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, // Async I/O
NULL); // template must be 0 for comm devices
if (m_hComm == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
// port not found
delete [] szPort;
delete [] szBaud;
return FALSE;
}
// set the timeout values
memset(&m_CommTimeouts, 0, sizeof(m_CommTimeouts));
memset(&m_dcb, 0, sizeof(m_dcb));
m_CommTimeouts.ReadIntervalTimeout = 1000;
m_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 1000;
m_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutConstant = 1000;
m_CommTimeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 1000;
m_CommTimeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutConstant = 1000;
// configure
if (SetCommTimeouts(m_hComm, &m_CommTimeouts))
{
if (GetCommState(m_hComm, &m_dcb))
{
if (BuildCommDCB(szBaud, &m_dcb))
{
if (SetCommState(m_hComm, &m_dcb))
; // normal operation... continue
else
return FALSE;//ProcessErrorMessage("SetCommState()");
}
else
return FALSE;//ProcessErrorMessage("BuildCommDCB()");
}
else
return FALSE;//ProcessErrorMessage("GetCommState()");
}
else
return FALSE;//ProcessErrorMessage("SetCommTimeouts()");
delete [] szPort;
delete [] szBaud;
// flush the port
PurgeComm(m_hComm, PURGE_RXCLEAR | PURGE_TXCLEAR | PURGE_RXABORT | PURGE_TXABORT);
return TRUE;
}
int SerialPort::WriteToPort( char *writeData, int WriteSize )//发送数据
{
BOOL bResult = TRUE;
DWORD BytesSent = 0;
// Clear buffer
PurgeComm(m_hComm, PURGE_RXCLEAR | PURGE_TXCLEAR | PURGE_RXABORT | PURGE_TXABORT);
bResult = WriteFile(m_hComm, writeData, WriteSize, &BytesSent, NULL);
if (!bResult)
{
DWORD dwError = GetLastError();
switch (dwError)
{
case ERROR_IO_PENDING:
{
// continue to GetOverlappedResults()
BytesSent = 0;
//bWrite = FALSE;
return -1;
break;
}
default:
{
// all other error codes
//port->ProcessErrorMessage("WriteFile()");
//return -1;
}
}
}
// end if(bWrite)
//Verify that the data size send equals what we tried to send
if (BytesSent != (DWORD)WriteSize) // Length of message to send)
{
//TRACE("WARNING: WriteFile() error.. Bytes Sent: %d; Message Length: %d\n", BytesSent, strlen((char*)port->m_szWriteBuffer));
return -1;
}
return BytesSent;
}
//----------------
int SerialPort::ReceiveChar( char *readBuff, int ReadSize )//接收数据
{
BOOL bRead = TRUE;
BOOL bResult = TRUE;
DWORD dwError = 0;
DWORD BytesRead = 0;
bResult = ReadFile(m_hComm, readBuff, ReadSize, &BytesRead, NULL);
if (!bResult)
{
switch (dwError = GetLastError())
{
case ERROR_IO_PENDING:
{
// asynchronous i/o is still in progress
// Proceed on to GetOverlappedResults();
//bRead = FALSE;
return -1;
break;
}
default:
{
// Another error has occured. Process this error.
//port->ProcessErrorMessage("ReadFile()");
break;
}
}
}
if (BytesRead != (DWORD)ReadSize)
{
PurgeComm(m_hComm, PURGE_RXCLEAR | PURGE_TXCLEAR);
return -1;
}
return BytesRead;
}
8、第7步骤中的代码复制后没有排版, 先按ctrl+a全选 然后再按alt+F8 自动排版
在stdafx.h中 引入头文件
#include <windows.h>
9、以下是Demo.cpp中的代码
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "SerialPort.h"
SerialPort m_serialPort = new SerialPort();
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
m_serialPort->setPortName(1);
m_serialPort->setBaud(9600);
m_serialPort->InitPort();
//一下是打印机的功能
char writeBuf[10];
writeBuf[0] = 0x0A;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)//循环发送 打印空的5行
{
m_serialPort->WriteToPort(writeBuf,1); //发送打印换行
}
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
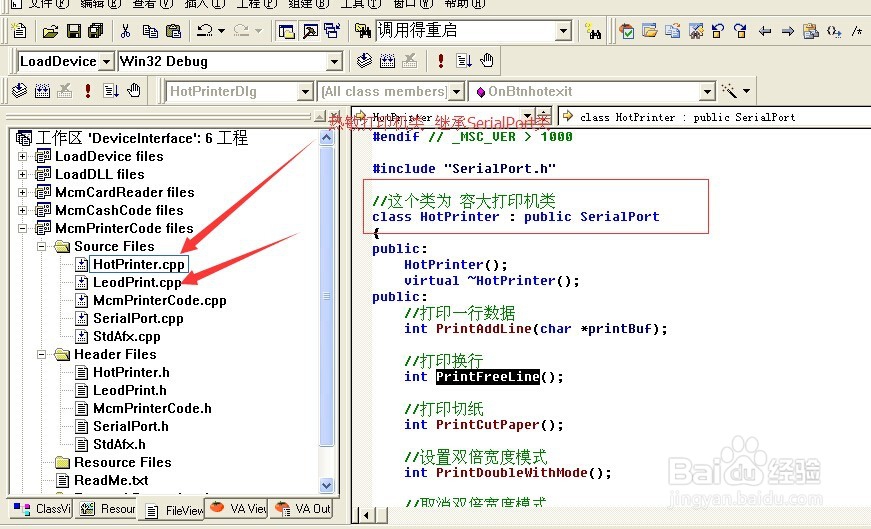
10、这个类封装好后可以将 SerialPort.h 和SerialPort.cpp文件放带MFC中调用,也可以在Win32程序中调用.
扩展功能,比如写一个热敏打印机的程序. 则添加一个HotPrinter类 继承这个类,这样管理起来比较方便.
比如我自己的热敏打印机这样写的,我就不写具体步骤了.