putchar的用法
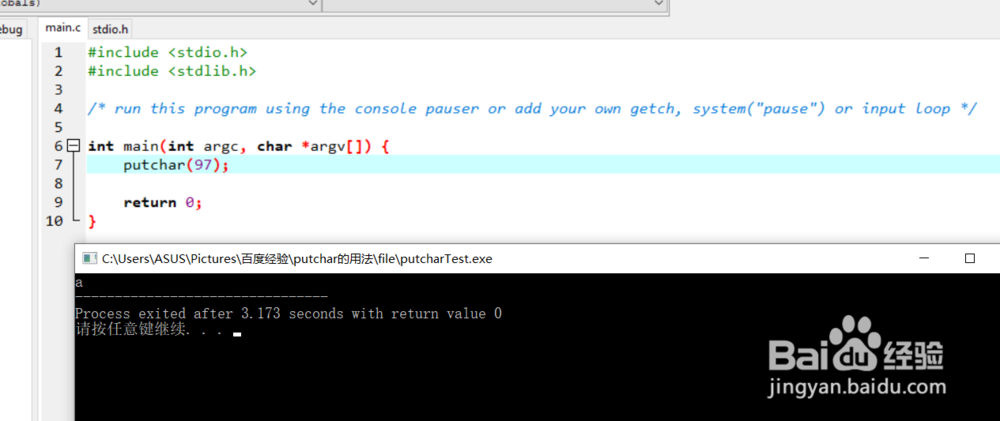
1、通过putchar获取指定数字的图形:
比如putchar(97);会输出英语字母a,标明ASCII码97对应小写字母a 。
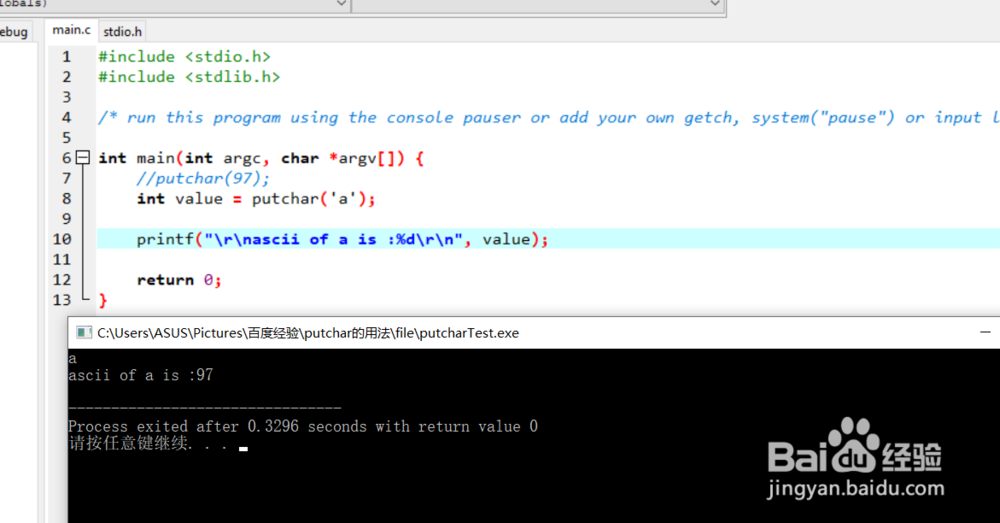
2、通过putchar获取指定字符的ASCII码:
asciiValue = putchar('a');
printf("ascii of a is :%d\r\n", asciiValue);
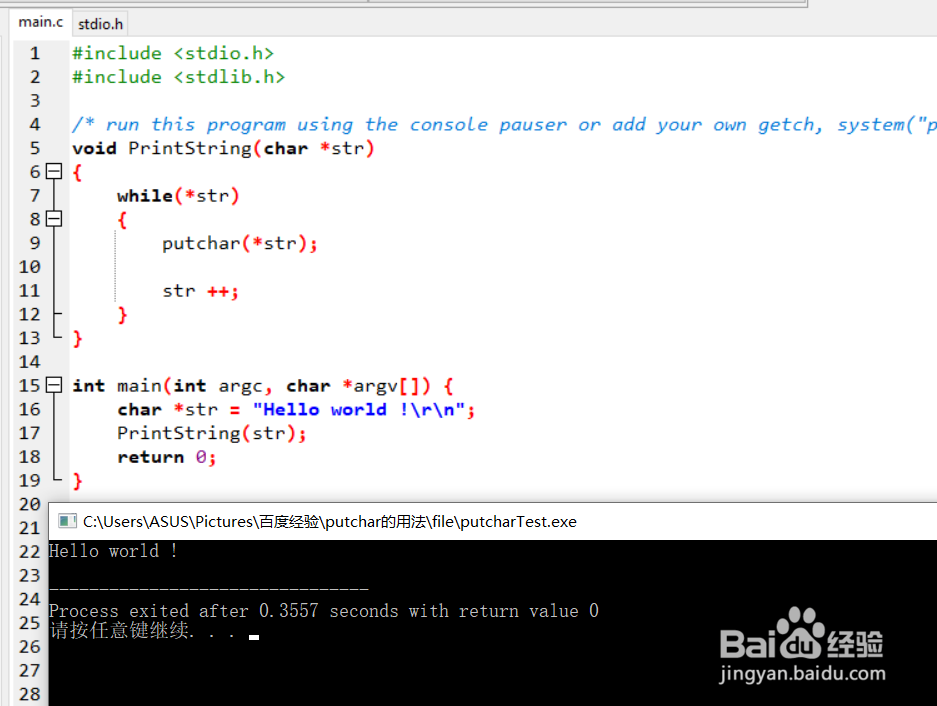
3、通过putchar实现字符串的打印函数:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
void PrintString(char *str)
{
while(*str)
{
putchar(*str);
str ++;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char *str = "Hello world !\r\n";
PrintString(str);
return 0;
}
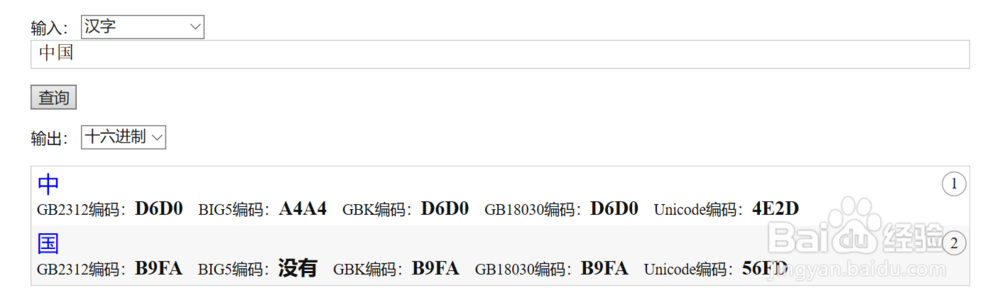
4、实际上putchar还可以用来输出汉字,但我们需要知道汉字的编码,具体百度查询,比如下面这个列出了汉字“中国”的GB2312编码、BIG5编码、GBK编码、GB18030编码、Unicode编码。
5、虽然putchar接收的是int型参数,不小于2字节,但是它实际是按照ASCII码处理的,即只具备一个字节的字符输出能力,所以对于占用2个字节的汉字需要分开输出:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
putchar(0xd6); //汉字"中" GB2312编码高字节
putchar(0xd0); //汉字"中" GB2312编码低字节
putchar(0xB9); //汉字"国" GB2312编码高字节
putchar(0xFA); //汉字"国" GB2312编码低字节
return 0;
}

6、总结:
1、putchar()可以接收数字和字符形式的参数。
2、putchar()的返回值指示了字符输出的状态,成功则返回对应字符的ASCII码值,失败后返回非ASCII码值。
3、对一个字符串遍历,依次调用putchar()可以实现字符串的输出。
4、在知道汉字编码的情况下,可以分两步调用putchar(),实现汉字输出。
