H2数据库存储文件
1、H2数据库的数据类型,见下图。这些类型基本和其他数据库的类型差不多,之所以要写这个经验,是因为我用到了它的CLOB类型。下面介绍一下CLOB怎么使用。

2、BLOB主要用于存储像文件或者图片这样的大数据。CLOB主要用于XML、HTML、Txt文件等。


3、现在的需求是表中某一列存放文件数据,文件内容通过Base64编码存储。
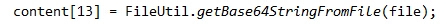
4、存入数据库时,我是将文件内容通过Base64编码存入的字符串。
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
public static String getBase64StringFromFile(File file) {
String result = "";
try {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int ch ;
while((ch = is.read()) != -1) {
baos.write(ch);
}
byte[] bs = baos.toByteArray();
result = Base64.encodeBase64String(bs);
is.close();
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.debug(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
return result;
}
这里的result就是Base64编码后的字符串了。

5、从数据库中读出来时,该列数据类型是CLOB,那怎么再显示这个文件呢?
Clob clob = (Clob) objs[0][14];
BufferedReader br = (BufferedReader) clob.getCharacterStream();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String rline = null;
while ((rline = br.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(rline);
}
String content = sb.toString();
这个content就是上步说的Base64编码后的字符串。
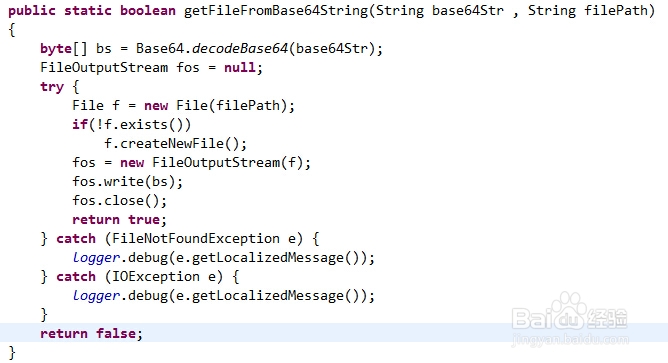
6、如果要还原该文件,还需要再Base64解码后再保存成文件。
public static boolean getFileFromBase64String(String base64Str , String filePath) {
byte[] bs = Base64.decodeBase64(base64Str);
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
File f = new File(filePath);
if(!f.exists())
f.createNewFile();
fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
fos.write(bs);
fos.close();
return true;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
logger.debug(e.getLocalizedMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.debug(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
return false;
}
这里的filePath就是我们还原之后的文件的路径,就可以看到还原后的文件了。
7、至此,应该对CLOB类型有了一定了解了,知道如何使用了吧。